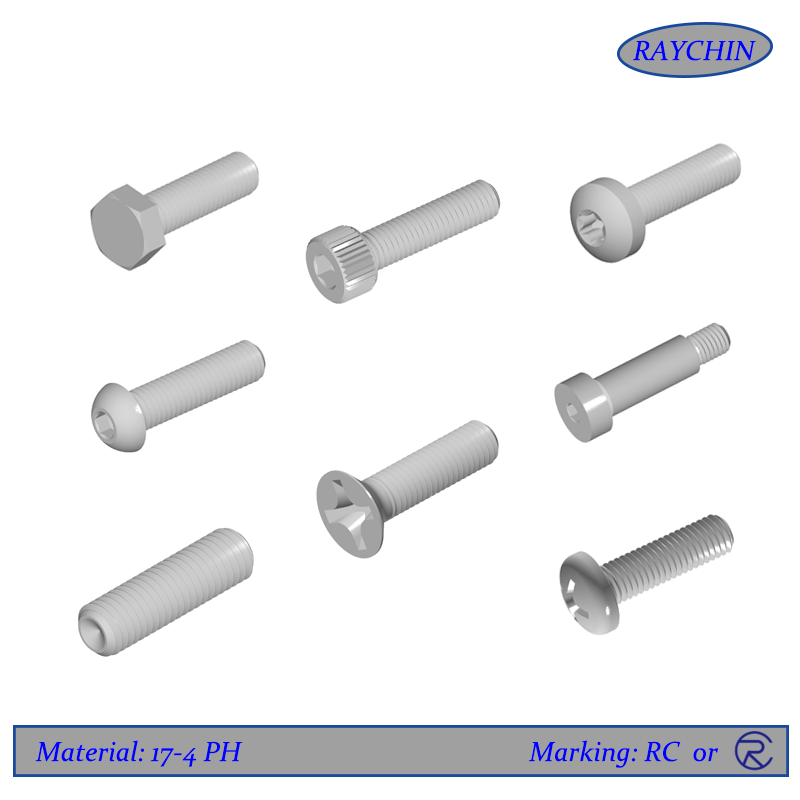
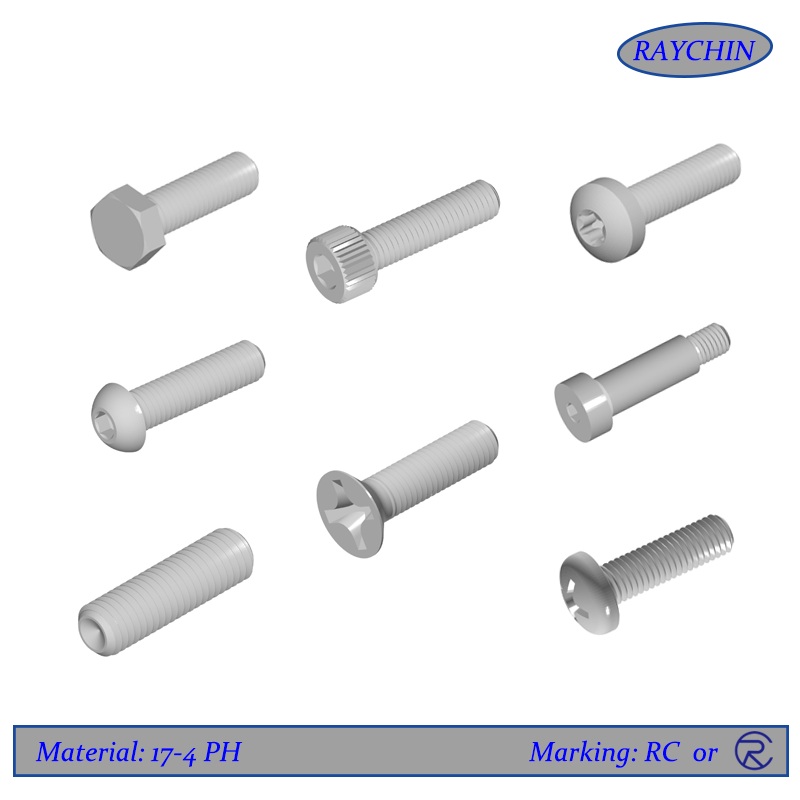
17-4 PH 12 Point Screws
17-4 PH 12 Point Screws
17-4 PH 12 point screws are made from a precipitation hardened stainless steel most known for its exceptional strength and its ability to maintain its mechanical properties to 600°F. Compared to 316 stainless steel, 17-4 PH screws yield strength is up over 4 times greater. When compared to Duplex 2205 screws, the yield strength of 17-4 PH can be up to 2-½ times greater.
17-4 12 point screws are available in 8 different aged (precipitation hardened) conditions offering a variety of mechanical properties.
An extremely strong precipitation hardened stainless steel
· Well suited for high strength applciaitons
· Up to 4x stronger than 316 stainless steel
· Maintains its mechanical strength up to 600°F
· 17-4PH Chemistry & Specifications
· 17-4PH 12 point screw features and benefits
· 17-4PH Datasheet
Resources: 17-4PH Torque Specs
17-4 PH Screw Types: 12 Point Screws, Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Cap Screws, Pan Head Screws, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws, Torx Screws, Vented Screws
17-4PH 12-Point Screw Features & Benefits
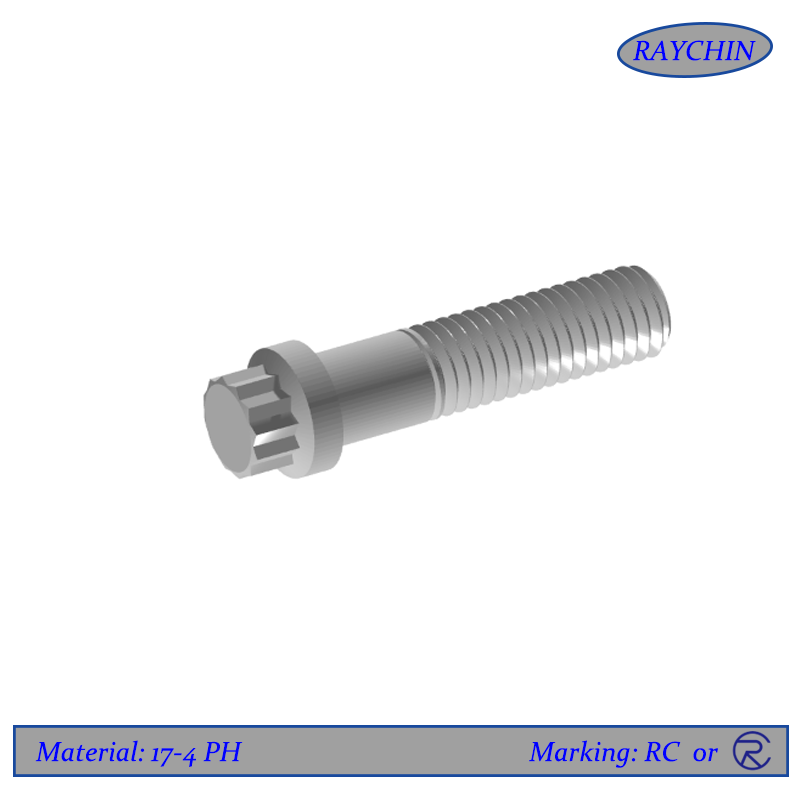
The driver of a 17-4PH 12-point screw uses two overlapped hexagon shapes, creating 12-points and a flanged underside. These are also referred to as ferry cap screws or 12 point flange screws. The advantages of this head style include:
· Higher torque capability compared to a socket head cap screw
· Lack of recess to trap fluid or debris.
· As the heads are generally smaller than a hex, 17-4PH 12-point screws are often used situations where installation space is tight and saving weight is critical.
The overall disadvantage is the extra cost involved in forming the heads.
The Controversy of 6 vs. 12 point Bolts
There is much debate over which bolt is better. Some say that the more points a nut or bolt has – such as a 12-point bolt - the less chance you have to round it off. And that the additional contact points of a 12 point screw give you more surface to apply load. While the jury is out as to the accuracy of this, it’s the application that should dictate whether the benefits of a 12 point screw out weight the additional costs of making them.
17-4PH Chemistry & Specifications
17-4PH Specifications: UNS S17400, AISI 630, ASTM A564-630, Werkstoff 1.4542, AMS 5604 Sheet, Strip and Plate, ASTM A 693 Plate
17-4PH | Fe | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mn | Si | Mo | Nb+Ta | C | P | S |
Min% |
| 15.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Max% | Bal | 17.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.50 | 0.45 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
ASTM F593, Grade 630
This specification covers seven groups of stainless steel alloys, with ASTM F593, Grade 630 applying 17-4PH. ASTM F593 Grade 630 covers the requirements for 17-4PH stainless steel bolts, hex cap screws, and studs sized 0.25 to 1.50 inches, inclusive, in nominal diameter. It is intended for common use and for service applications requiring general corrosion resistance.
| Full-Size Tests | Machined Specimen Tests |
Stainless Steel Alloy Group | Condition | Alloy Mechanical Property Marking | Nominal Diameter (inches) | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Yield Strength (ksi) | Rockwell Hardness | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Yield Strength | Elongation % |
7(630) | AH | F593U | 1/4 to 1.5 IN | 135 to 170 | 105 | C28 to38 | 135 | 105 | 16 |
Common 17-4 Fastener Conditions: Aged Conditions vs Tensile Strength
Aged Condition | Ultimate Tensile (ksi) | Yield Strength at 0.2% Offset (ksi) | Elongation % | Hardness Rc |
H900 | 200 | 185 | 14 | 40-47 |
H925 | 190 | 175 | 14 | 38-45 |
H1025 | 170 | 165 | 15 | 35-42 |
H1075 | 165 | 150 | 16 | 33-39 |
H1100 | 150 | 135 | 17 | 32-38 |
H115C | 145 | 125 | 19 | 28-37 |
H1150-M | 125 | 85 | 22 | 26-36 |
Annealed | 160 | 145 | 5 | ~35 |