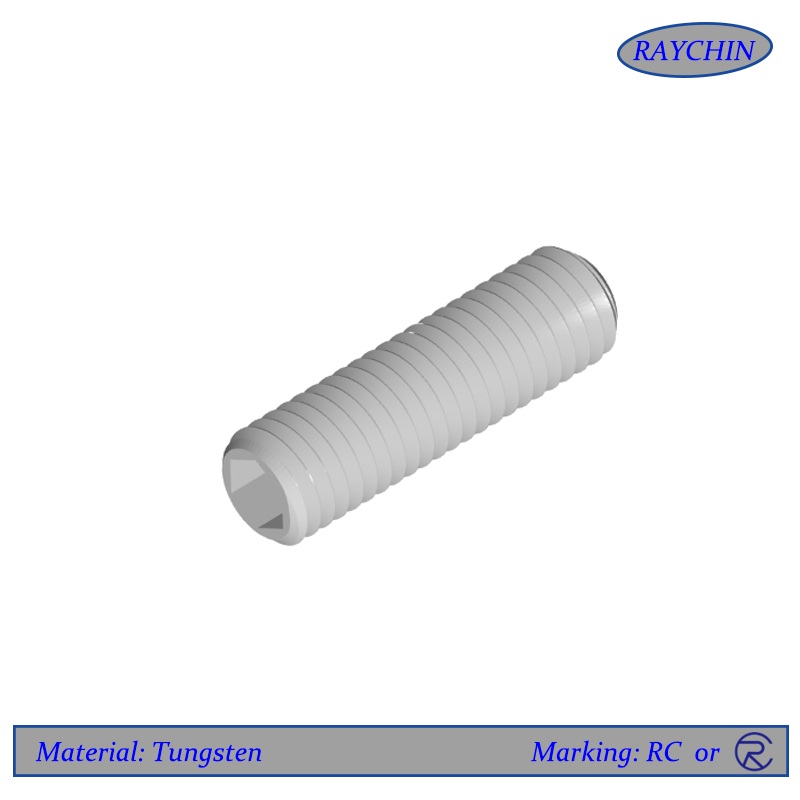
Tungsten Set Screws
Tungsten Set Screws
Tungsten set screws are known for their extreme high density; because of this unique attribute, they are often used for balancing rotating parts. Tungsten’s high mass also makes these screws radiopaque. This allows tungsten screws to block radiation and show up well on x-rays – even better than lead. Another unique attribute of tungsten is its extrmely high melting point of 3420°C. The high temperature stability of tungsten set screws make them ideal for some of the hottest vacuum furnace environments. Beyond their high mass and temperature stability, tungsten fasteners are also very corrosion resistant.
Tungsten set screws are usually made from tungsten alloys per ASTM B777, and range from 90% to 97% pure tungsten, alloyed with nickel and copper or nickel and iron.

Ultra-high density & high temperature / strength stability
· Very high density of 19.3 gm/cc
· Radiopaque to x-rays and other radiation
· High strength at extreme high temperatures (vacuum)
· Excellent corrosion resistance
· Mechanical properties of tungsten set screws
· Tungsten material datasheet
· Set screw features & benefts
Applications
· The aerospace industry depends on the tungsten set screws for their combination of high density and mechanical strength which allows them to reduce the physical size of components, offering greater control of weight distribution for propellers, inertial systems and fluid control systems to name a few.
· The heat treating / furnace industry uses tungsten screws in high temperature vacuum furnaces due to tungstens great high temperature strength & stability.
· The oil & gas industry uses tungsten screws for radiation shielding properties to protect equipment used in oil and gas detection, as well as down hole logging for density and ability to withstand intense hydrostatic pressure
· Tungsten set screws also play a role in the medical community for their low magnetic properties as well as their radiopaque properties.
Resources: Tungsten Torque Specs
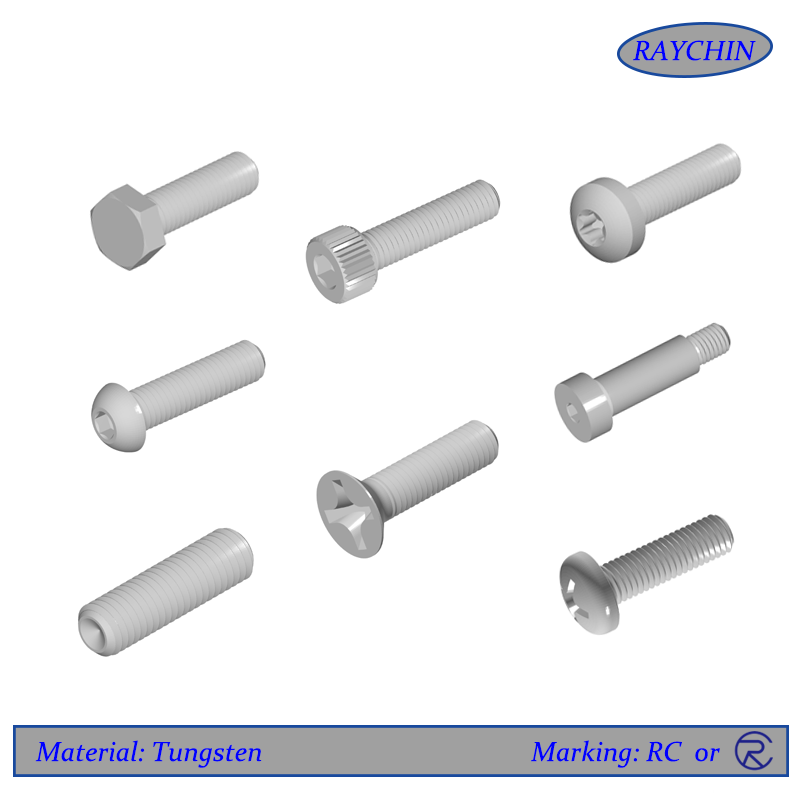
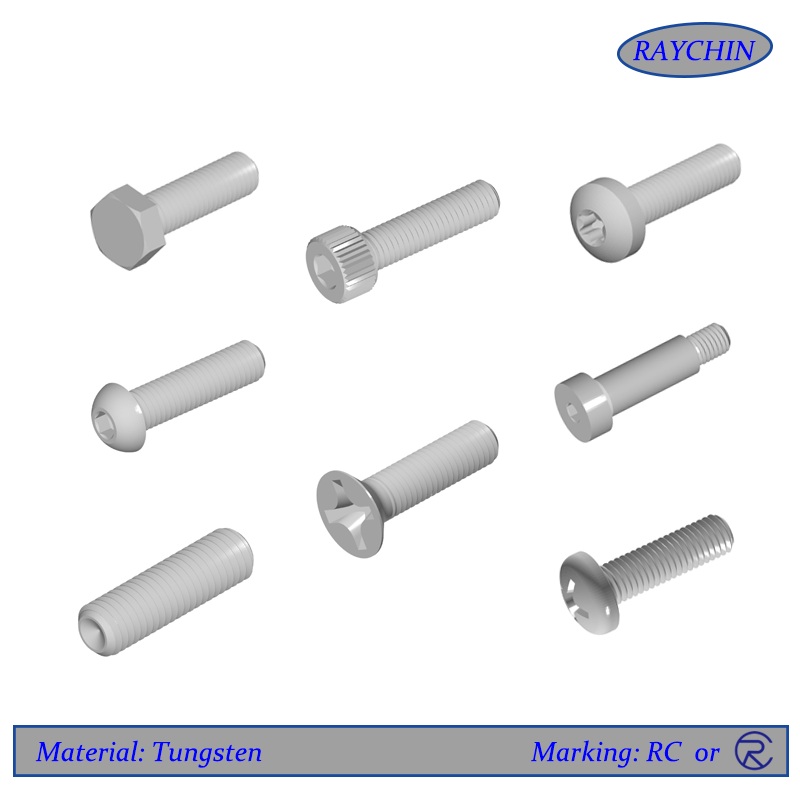
Tungsten Screw Types: Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Head Cap Screws, Pan Head, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws
Tungsten Set Screw Features & Benefits
Tungsten set screws are unique in that they have no screw head, meaning that they have no protruding part past the threaded shaft. They are thread only and are available with a socket or slotted driver insert at one end. Set screws are used to secure an object within or against another object. Typically they secure a rotating part such as a gear or shaft. Tungsten set screws are driven through a threaded hole in the rotating part until it is tight against the inner object, preventing from moving relative to the outer object. Set screws are available with various points depending on the application.
Cup Point
This is the most commonly used set screw and is identified by a cup-shaped indentation on one end. Tungsten cup points are typically used for a quick, semi-permanent or permanent applications where it is acceptable to cut the cup point edge of the screw.
Cone Point
A cone point is easily identifiable by its sharp cone-shaped point – just like an ice cream cone. Tungsten cone point set screws deliver the strongest clamping force due to the deep penetration of the point. As a result they are used for permanent assembly.
Flat Point
The cheapest and simplest of the set screw point styles, this screw has a flat surface on the bottom of the screw. This type is used when you need the ability to frequently change parts and require minimal shaft deformation.
Tungsten Chemistry & Specifications
Tungsten Specifications: ASTM B777, Mil Spec T-21014D
Tungsten Alloy ASTM-B777 | Class 1 | Class2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | CP Tungsten |
Material Composition | 90% W 6%Ni 4%Cu | 92.5% W 5.25% Ni 2.25% Fe | 95% W 3.5% Ni 1.5% Cu | 97% W 2.1% Ni 0.9% Fe | 99.95% W |
Density | 17 gm/cc | 17.5 gm/cc | 18 gm/cc | 18.5 gm/cc | 19.3 gm/cc |
Density; Ibs/in3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.697 |
Mil. Spec. T-21014 D | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 |
|
Type | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III |
|
Hardness; Rockwell C | 24.0 | 26.0 | 27.0 | 28.0 | 31.0 |
Ultimate Tensile Strength; PSI | 94,000 | 110,000 | 94,000 | 100,000 | 142,000 |
Yield Strength, .2% Offset; PSI | 75,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 | 109,000 |
Modulus of Elasticity; PSI | 40X10E6 | 47xlOE6 | 45 x10E6 | 53 X10E6 | 58x10E6 |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion x | 5.4 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.2 |
Electrical Conductivity; %IACS | 14 | 13 | 16 | 17 | 18 |