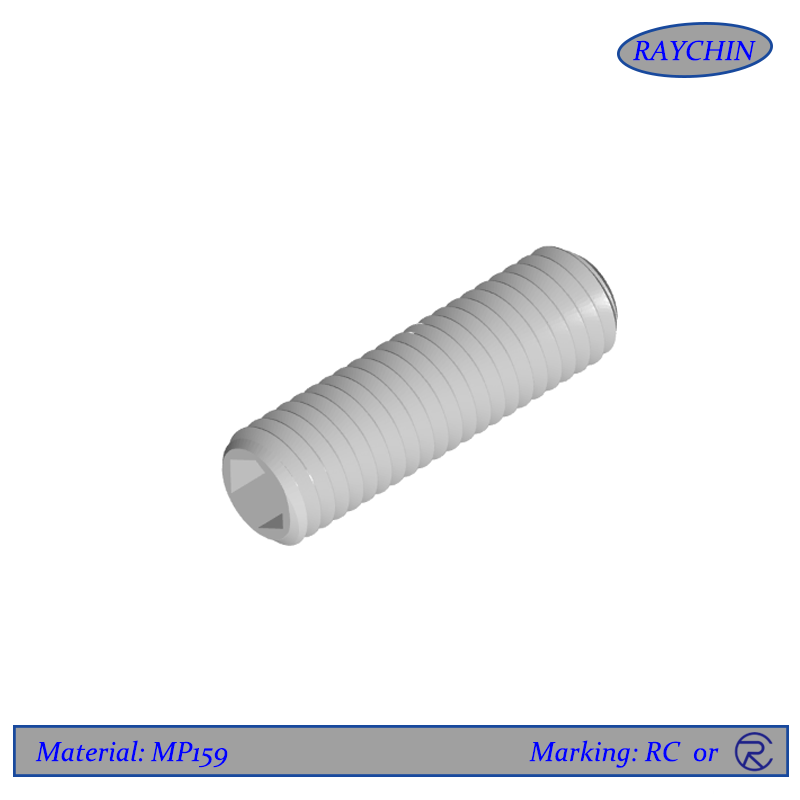
MP159 Set Screws
Brand RAYCHIN
Product origin China
Delivery time 5-35 DAYS
As aerospace engineering advances, so must the materials to meet the technological requirements of this industry. Screws made from MP159 have been developed to provide a solution to high temperature, high strength components. MP159 set screws offer strength capabilities similar to other Cobalt Alloys (MP35N) but can be used at much higher temperatures - up to 1100°F, compared to MP35N’s usable limit of 800F. In addition, MP159 set screws can be used beyond 1100°F in short term situations.
MP159 Set Screw
As aerospace engineering advances, so must the materials to meet the technological requirements of this industry. Screws made from MP159 have been developed to provide a solution to high temperature, high strength components. MP159 set screws offer strength capabilities similar to other Cobalt Alloys (MP35N) but can be used at much higher temperatures - up to 1100°F, compared to MP35N’s usable limit of 800F. In addition, MP159 set screws can be used beyond 1100°F in short term situations.
Ultra-strength combined with extreme temperature capabilities
· Extreme high strength properties up to 275 ksi ultimate tensile.
· Maintains superior strength to 1100°F.
· MP159 chemisty and specification
· Datasheet for MP159
· MP159 set screw features & benefits
Key Benefits
· High ultimate tensile strength of 275 ksi and yield strength of 265 ksi (Cold Worked and Age Hardened) combined with excellent ductility and toughness
· Similar corrosion resistance compared to MP35N which is usable in mineral acids, hydrogen sulfide, seawater and salt spray environments.
· Excellent fatigue resistance and creep strength at elevated temperatures
· Excellent resistance to crevice corrosion, stress corrosion cracking and hydrogen embrittlement
Applications
· The aerospace industry relies on MP159 screws for its most advanced gas turbine and jet engines, rocket boosters and jet propulsion systems.
· Power generation and chemical processing utilize MP159 set screws for applications that demand high strength at extreme temperatures.
Resources: MP159 Torque Spec
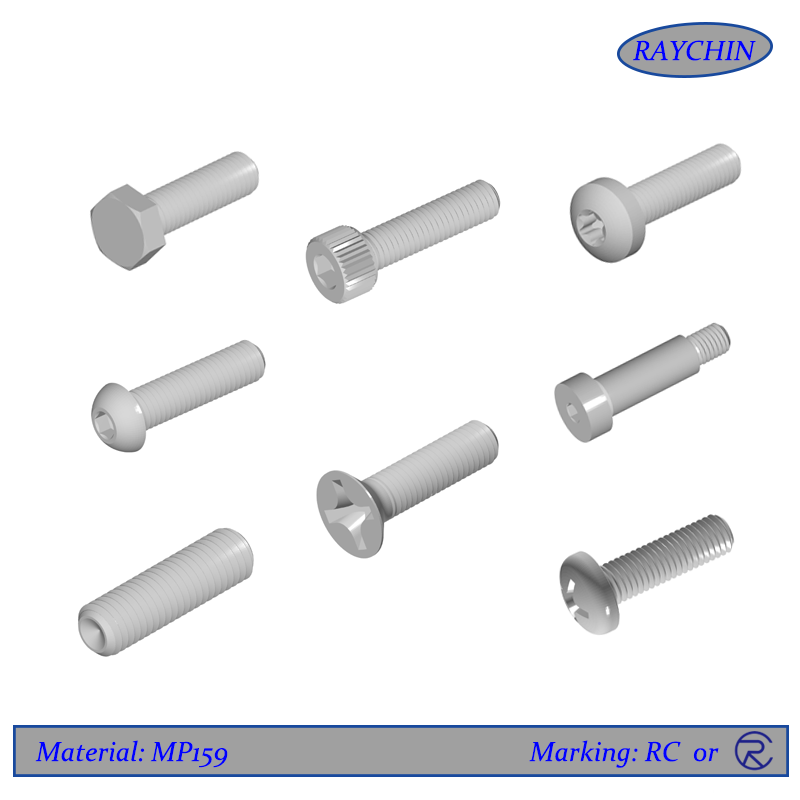
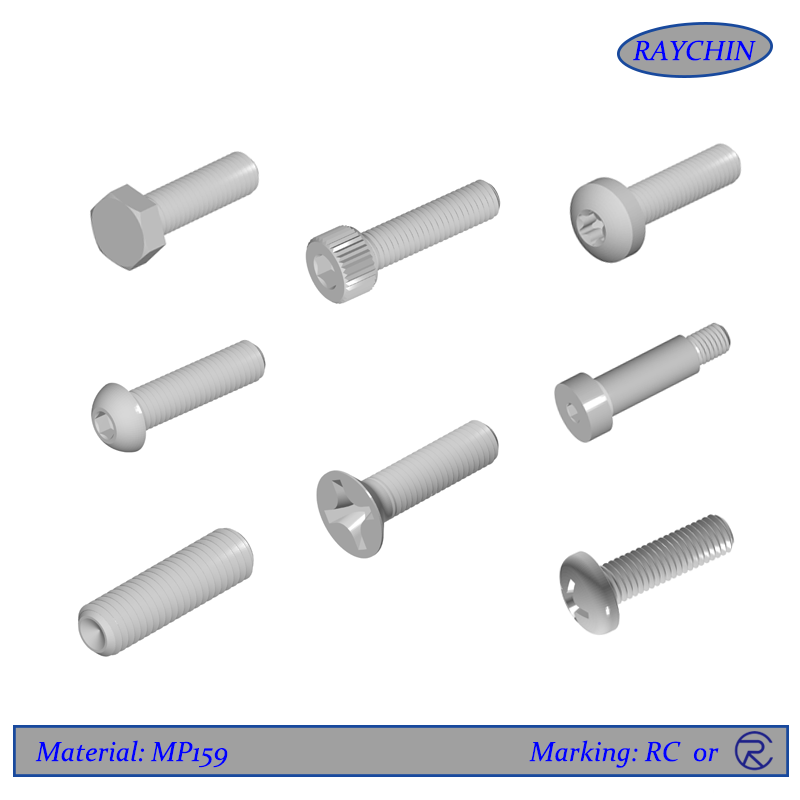
MP159 Screw Types: 12 Point Screws, Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Cap Screws, Hex Cap Screws, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws
MP159 Set Screw Features & Benefits
MP159 set screws are unique in that they have no screw head, meaning that they have no protruding part past the threaded shaft. They are thread only and are available with a socket or slotted driver insert at one end. Set screws are used to secure an object within or against another object. Typically they secure a rotating part such as a gear or shaft. MP159 set screws are driven through a threaded hole in the rotating part until it is tight against the inner object, preventing from moving relative to the outer object. Set screws are available with various points depending on the application.
Cup Point
This is the most commonly used set screw and is identified by a cup-shaped indentation on one end. MP159 cup points are typically used for a quick, semi-permanent or permanent applications where it is acceptable to cut the cup point edge of the screw.
Cone Point
A cone point is easily identifiable by its sharp cone-shaped point – just like an ice cream cone. MP159 cone point set screws deliver the strongest clamping force due to the deep penetration of the point. As a result they are used for permanent assembly.
Flat Point
The cheapest and simplest of the set screw point styles, this screw has a flat surface on the bottom of the screw. This type is used when you need the ability to frequently change parts and require minimal shaft deformation.
MP159 Chemistry and Specifications
MP159N Specifications: UNS R30159
MP159 | Co | Ni | Cr | Fe | Mo | Ti | Nb | Al |
Typical% | 35.7 | 25.5 | 19 | 9 | 7 | 3 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
MP159 High Strength Data
Cold Worked, 48% +1225eF (663eC)/4 hrs/AC | |
UTSksi(MPa) | 275(1895) |
Yield strength at 0.2% ksi (MPa) | 265(1825) |
% Elogation | 8 |
%RA | 35 |
Shear strength ksi (MPa) Per MIL- STD-1312 | 138(951) |