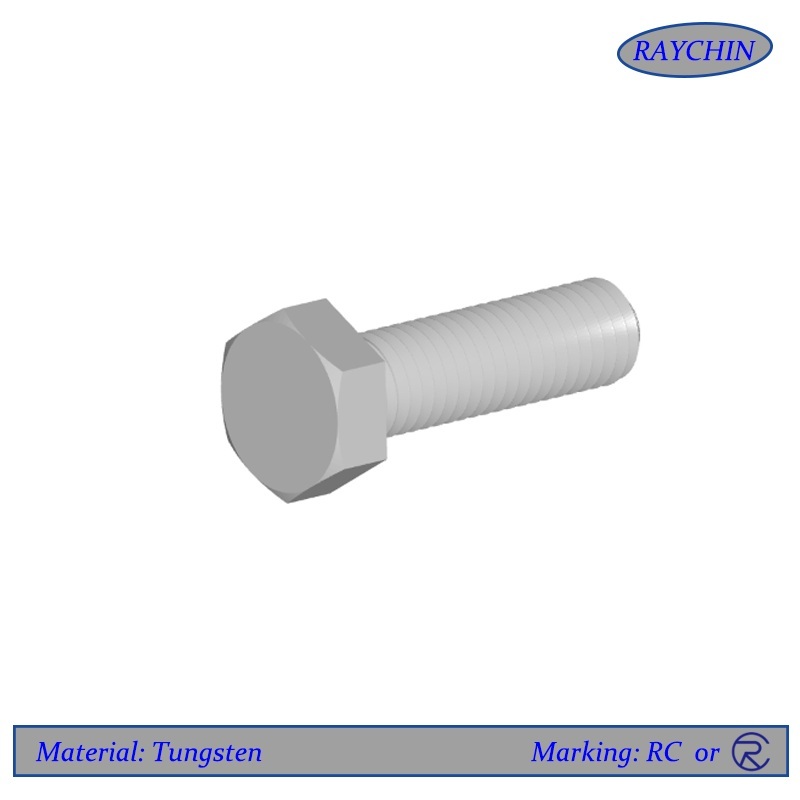
Tungsten Hex Cap Screws
Tungsten Hex Head Cap Screws
Tungsten hex head cap screws are known for their extreme high density; because of this unique attribute, they are often used for balancing rotating parts. Tungsten’s high mass also makes these hex heads radiopaque. This allows tungsten screws to block radiation and show up well on x-rays – even better than lead. Another unique attribute of tungsten is its extrmely high melting point of 3420°C. The high temperature stability of tungsten fasteners make them ideal for some of the hottest vacuum furnace environments. Beyond their high mass and temperature stability, tungsten hex head cap screws are also very corrosion resistant.
Tungsten hex head cap screws are usually made from tungsten alloys per ASTM B777, and range from 90% to 97% pure tungsten, alloyed with nickel and copper or nickel and iron.
Ultra-high density & high temperature / strength stability
· Very high density of 19.3 gm/cc
· Radiopaque to x-rays and other radiation
· High strength at extreme high temperatures (vacuum)
· Excellent corrosion resistance
· Mechanical properties of tungsten screws
· Tungsten material datasheet
· Hex head cap screw features & benefits
Applications
· The aerospace industry depends on the tungsten screws for their combination of high density and mechanical strength which allows them to reduce the physical size of components, offering greater control of weight distribution for propellers, inertial systems and fluid control systems to name a few.
· The heat treating / furnace industry uses tungsten hex head cap screws in high temperature vacuum furnaces due to tungstens great high temperature strength & stability.
· The oil & gas industry uses tungsten screws for radiation shielding properties to protect equipment used in oil and gas detection, as well as down hole logging for density and ability to withstand intense hydrostatic pressure
· Tungsten hex head cap screws also play a role in the medical community for their low magnetic properties as well as their radiopaque properties.
Resources: Tungsten Torque Specs
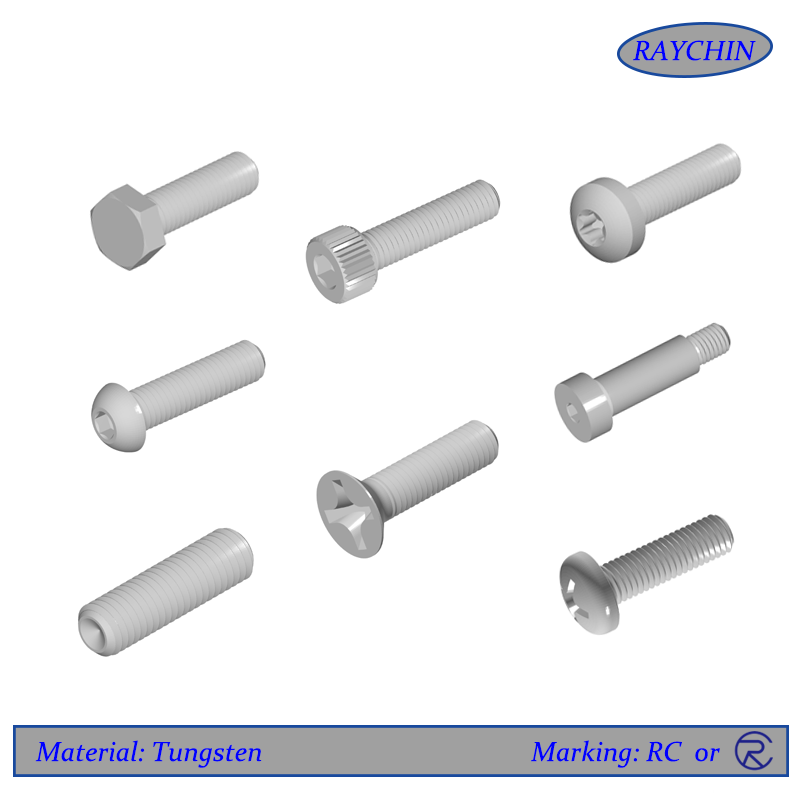
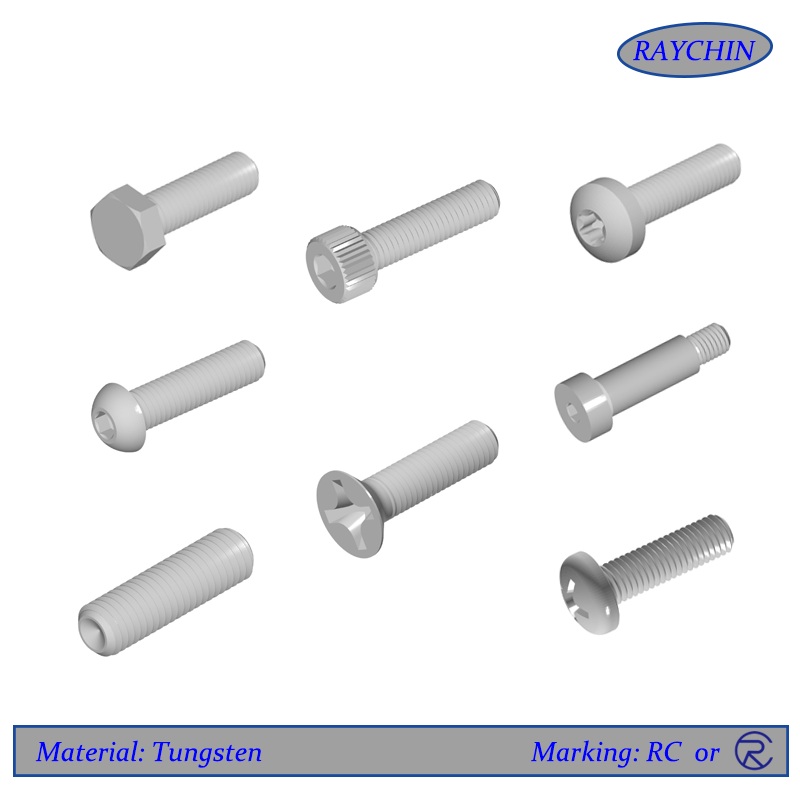
Tungsten Screw Types: Button Head Cap Screws, Flat Head Screws, Hex Head Cap Screws, Pan Head, Set Screws, Socket Head Cap Screws, Tamper Resistant Security Screws
Tungsten Hex Head Cap Screw Features and Benefits
It is important to differentiate between a tungsten hex head cap screw and hex head bolt. Often people assume they are the same, but they are actually very different fasteners in terms of how they are manufactured, as well as from an application perspective. Regardless of your choice, tungsten hex heads offer strong, stable joints because of their large head service.
The Hex Comparison
Hex Head Cap Screw | Hex Head Bolts |
· Precise applications where tight tolerances on the body dimensions are required. · Features flat washer facing under the bolt head. · Also called a finished hex bolt. | · Appropriate for when mechanical properties are more important than dimensional tolerances. · Hex bolts have a flat end and lack the washer face under the head. |
Tungsten Hex Head Cap Screw Advantages
The most important feature of a tungsten hex head cap screws is that it has a larger bearing surface area which provide better clamping pressure than other type of fastener such as a socket head cap screw. Additionally, since debris build up is less of an issue with this style of fastener verses a socket head cap screw, they are ideal of dirty applications where particles could clog up a socket. Though tungsten socket heads are typically used for tight access applications, hex heads can be a better choice when there is only side clearance available for tightening.
Tungsten Chemistry & Specifications
Tungsten Specifications: ASTM B777, Mil Spec T-21014D
Tungsten Alloy ASTM-B777 | Class 1 | Class2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | CP Tungsten |
Material Composition | 90% W 6%Ni 4%Cu | 92.5% W 5.25% Ni 2.25% Fe | 95% W 3.5% Ni 1.5% Cu | 97% W 2.1% Ni 0.9% Fe | 99.95% W |
Density | 17 gm/cc | 17.5 gm/cc | 18 gm/cc | 18.5 gm/cc | 19.3 gm/cc |
Density; Ibs/in3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.697 |
Mil. Spec. T-21014 D | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 |
|
Type | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III |
|
Hardness; Rockwell C | 24.0 | 26.0 | 27.0 | 28.0 | 31.0 |
Ultimate Tensile Strength; PSI | 94,000 | 110,000 | 94,000 | 100,000 | 142,000 |
Yield Strength, .2% Offset; PSI | 75,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 | 109,000 |
Modulus of Elasticity; PSI | 40X10E6 | 47xlOE6 | 45 x10E6 | 53 X10E6 | 58x10E6 |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion x | 5.4 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 4.2 |
Electrical Conductivity; %IACS | 14 | 13 | 16 | 17 | 18 |